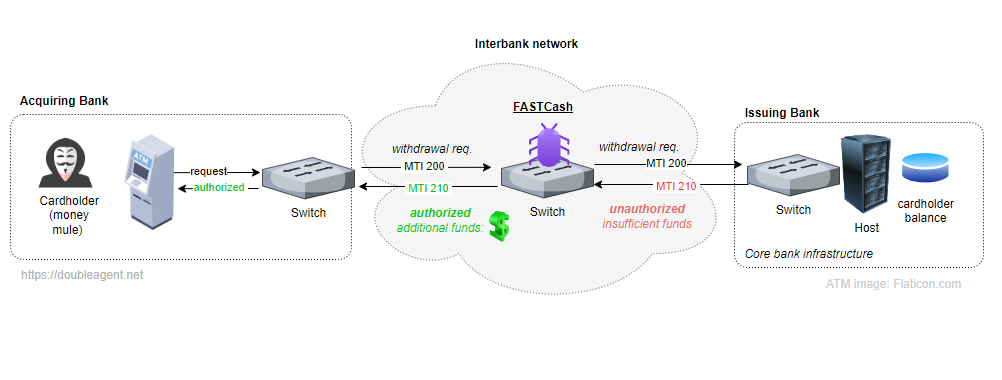
The malware resides in the userspace portion of the interbank switch connecting the issuing domain and the acquiring domain. When a compromised card is used to make a fraudulent translation, FASTCash tampers with the messages the switch receives from issuers before relaying it back to the merchant bank. As a result, issuer messages denying the transaction are changed to approvals.
The following diagram illustrates how FASTCash works:
The switches chosen for targeting run misconfigured implementations of ISO 8583a messaging standard for financial transactions. The misconfigurations prevent message authentication mechanisms, such as those used by field 64 as defined in the specification, from working. As a result, the tampered messages created by FASTCash aren’t detected as fraudulent.
“FASTCash malware targets systems that ISO8583 messages at a specific intermediate host where security mechanisms that ensure the integrity of the messages are missing, and hence can be tampered,” haxrob wrote. “If the messages were integrity protected, a field such as DE64 would likely include a MAC (message authentication code). As the standard does not define the algorithm, the MAC algorithm is implementation specific.”
The researcher went on to explain:
FASTCash malware modifies transaction messages in a point in the network where tampering will not cause upstream or downstream systems to reject the message. A feasible position of interception would be where the ATM/PoS messages are converted from one format to another (For example, the interface between a proprietary protocol and some other form of an ISO8583 message) or when some other modification to the message is done by a process running in the switch.
CISA said that BeagleBoyz—one of the names the North Korean hackers are tracked under—is a subset of HiddenCobra, an umbrella group backed by the government of that country. Since 2015, BeagleBoyz has attempted to steal nearly $2 billion. The malicious group, CISA said, has also “manipulated and, at times, rendered inoperable, critical computer systems at banks and other financial institutions.”
The haxrob report provides cryptographic hashes for tracking the two samples of the newly discovered Linux version and hashes for several newly discovered samples of FASTCash for Windows.